Chapter 8
INTRODUCTION TO STRUCTURED QUERY LANGUAGE (SQL)
Exercise:
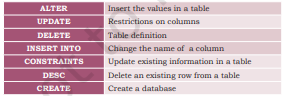
1. Match the following clauses with their respective functions.
2. Choose appropriate answer with respect to the following code snippet.
CREATE TABLE student ( name CHAR(30),
student_id INT,
gender CHAR(1),
PRIMARY KEY (student_id) );
a) What will be the degree of student table?
i) 30
ii) 1
iii) 3
iv) 4
Answer:
b) What does ‘name’ represent in the above code snippet?
i) a table
ii) a row
iii) a column
iv) a database
Answer:
c) What is true about the following SQL statement? SelecT * fROM student;
i) Displays contents of table ‘student’
ii) Displays column names and contents of table ‘student’
iii) Results in error as improper case has been used
iv) Displays only the column names of table ‘student’
Answer:
d) What will be the output of following query?
INSERT INTO student
VALUES (“Suhana”,109,’F’), VALUES (“Rivaan”,102,’M’), VALUES (“Atharv”,103,’M’), VALUES (“Rishika”,105,’F’), VALUES (“Garvit”,104,’M’), VALUES (“Shaurya”,109,’M’);
i) Error
ii) No Error
iii) Depends on compiler
iv) Successful completion of the query
Answer:
e) In the following query how many rows will be deleted? DELETE student WHERE student_id=109;
i) 1 row
ii) All the rows where student ID is equal to 109
iii) No row will be deleted
iv) 2 rows
Answer:
3. Fill in the blanks:
a) ____ declares that an index in one table is related to that in another table.
i) Primary Key
ii) Foreign Key
iii) Composite Key
iv) Secondary Key
Answer:
b) The symbol Asterisk (*) in a select query retrieves __.
i) All data from the table
ii) Data of primary key only
iii) NULL data
iv) None of the mentioned
Answer:
4. Consider the following MOVIE database and answer the SQL queries based on it
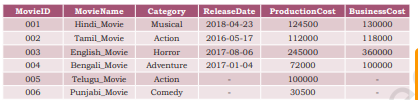
a) Retrieve movies information without mentioning their column names.
Answer:
b) List business done by the movies showing only MovieID, MovieName and BusinessCost.
Answer:
c) List the different categories of movies.
Answer:
d) Find the net profit of each movie showing its ID, Name and Net Profit. (Hint: Net Profit = BusinessCost – ProductionCost) Make sure that the new column name is labelled as NetProfit. Is this column now a part of the MOVIE relation. If no, then what name is coined for such columns? What can you say about the profit of a movie which has not yet released? Does your query result show profit as zero?
Answer:
e) List all movies with ProductionCost greater than 80,000 and less than 1,25,000 showing ID, Name and ProductionCost.
Answer:
f) List all movies which fall in the category of Comedy or Action.
Answer:
g) List the movies which have not been released yet.
Answer:
5. Suppose your school management has decided to conduct cricket matches between students of class XI and Class XII. Students of each class are asked to join any one of the four teams — Team Titan, Team Rockers, Team Magnet and Team Hurricane. During summer vacations, various matches will be conducted between these teams Help your sports teacher to do the following:
a) Create a database “Sports”.
Answer:
b) Create a table “TEAM” with following considerations:
i) It should have a column TeamID for storing an integer value between 1 to 9, which refers to unique identification of a team.
ii) Each TeamID should have its associated name (TeamName), which should be a string of length not less than 10 characters.
Answer:
c) Using table level constraint, make TeamID as primary key.
Answer:
d) Show the structure of the table TEAM using SQL command.
Answer:
e) As per the preferences of the students four teams were formed as given below. Insert these four rows in
TEAM table:
Row 1: (1, Team Titan)
Row 2: (2, Team Rockers)
Row 3: (3, Team Magnet)
Row 4: (4, Team Hurricane)
Answer:
f) Show the contents of the table TEAM.
Answer:
g) Now create another table below. MATCH_DETAILS and insert data as shown in table. Choose appropriate domains and constraints for each attribute.
Table: MATCH_DETAILS
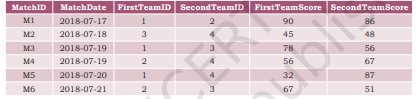
Answer:
h) Use the foreign key constraint in the MATCH_ DETAILS table with reference to TEAM table so that MATCH_DETAILS table records score of teams existing in the TEAM table only.
Answer:
6. Using the sports database containing two relations (TEAM, MATCH_DETAILS), answer the following relational algebra queries.
a) Retrieve the MatchID of all those matches where both the teams have scored > 70.
Answer:
b) Retrieve the MatchID of all those matches where FirstTeam has scored < 70 but SecondTeam has scored > 70.
Answer:
c) Find out the MatchID and date of matches played by Team 1 and won by it.
Answer:
d) Find out the MatchID of matches played by Team 2 and not won by it.
Answer:
e) In the TEAM relation, change the name of the relation to T_DATA. Also change the attributes TeamID and TeamName to T_ID and T_NAME respectively.
Answer:
7. Differentiate between the following commands:
a) ALTER and UPDATE
b) DELETE and DROP
Answer:
8. Create a database called STUDENT_PROJECT having the following tables. Choose appropriate data type and apply necessary constraints.
Table: STUDENT

- The values in Stream column can be either Science, Commerce, or Humanities.
- The values in Section column can be either I or II.
Table: PROJECT_ASSIGNED

a) Populate these tables with appropriate data.
b) Write SQL queries for the following.
c) Find the names of students in Science Stream.
d) What will be the primary keys of the three tables?
e) What are the foreign keys of the three relations?
f) Finds names of all the students studying in class ‘Commerce stream’ and are guided by same teacher, even if they are assigned different projects.
Answer:
9. An organization ABC maintains a database EMPDEPENDENT to record the following details about its employees and their dependents. EMPLOYEE(AadhaarNo, Name, Address, Department, EmpID) DEPENDENT(EmpID, DependentName, Relationship) Use the EMP-DEPENDENT database to answer the following SQL queries:
a) Find the names of employees with their dependent names. b) Find employee details working in a department, say, ‘PRODUCTION’. c) Find employee names having no dependent d) Find names of employees working in a department, say, ‘SALES’ and having exactly two dependents.
Answer:
10. A shop called Wonderful Garments that sells school uniforms maintain a database SCHOOL_UNIFORM as shown below. It consisted of two relations — UNIFORM and PRICE. They made UniformCode as the primary key for UNIFORM relation. Further, they used UniformCode and Size as composite keys for PRICE relation. By analysing the database schema and database state, specify SQL queries to rectify the following anomalies
a) The PRICE relation has an attribute named Price. In order to avoid confusion, write SQL query to change the name of the relation PRICE to COST.
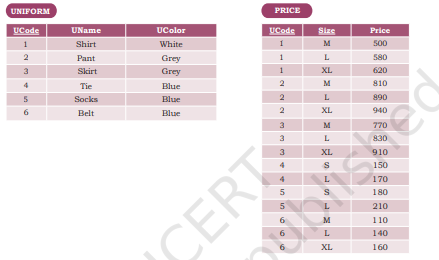
b) M/S Wonderful Garments also keeps handkerchiefs of red color, medium size of `100 each. Insert this record in COST table.
Answer:
c) When you used the above query to insert data, you were able to enter the values for handkerchief without entering its details in the UNIFORM relation. Make a provision so that the data can be entered in COST table only if it is already there in UNIFROM table.
Answer:
d) Further, you should be able to assign a new UCode to an item only if it has a valid UName. Write a query to add appropriate constraint to the SCHOOL_ UNIFORM database.
Answer:
e) ALTER table to add the constraint that price of an item is always greater than zero.
Answer: